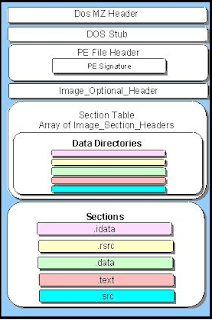
Imports are functions that are used in 1 program that are stored in a different program, usually common functionality commonly used by other programs.
Imports and export functions are usually used so that people do not need to recreate their own codes over and over again when coding other programs.
The import functions can give you an idea of what the program can do, and most probably will be running. Internal functions are intended to be called only from within the DLL where they are defined.
The exported functions are intended to be called by other modules, as well as from within the DLL where they are defined.
LoadLibrary, GetProcAddress, LdrGetProcAddress and LdrLoadDll are usually used to import linked functions, when these functions are used you cannot tell which functions are being linked to the program. ServiceMain function makes a program to run as a service.
Some popular DLL that are commonly seen:
- Kernel32.dll - access memory, files and hardware
- Advapi32.dll - advance core windows component such as service manager and registry
- User32.dll - user interface components, such as buttons, scoll bar
- Gdi32.dll - display and graphics
- Ntdll.dll - hiding functionality
- shell32.dll - ability to launch other programs
- WSock32.dll - networking related
- Ws2_32.dll - networking related
- Wininet.dll - high level network protocol, FTP, HTTP, NTP
Following picture shows a list of functions, more information please check on MSDN Online.
Tools to be used to find out the dlls used and the import/export functions within:
- Dependency Walker
- IDA PRO
Source: Practical Malware Analysis,
MSDN Microsoft